
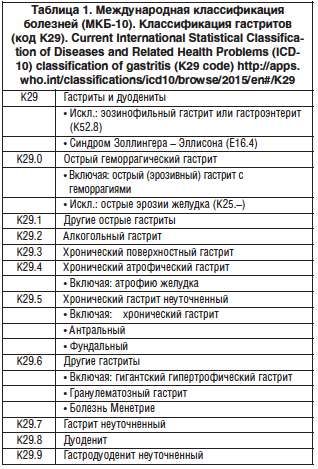
Gastric intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia, unspecified site Gastric intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia, involving multiple sites Gastric intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia, involving the cardia Gastric intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia, involving the fundus pylori as the cause of diseases classified to other chapters. Gastric intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia, involving the body (corpus) ICD-10-CA and CCI classifications were first introduced in 2001. Gastric intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia, involving the antrum Gastric intestinal metaplasia, unspecified The October 2021 updates will include 10 new codes in two new subcategories for gastric intestinal metaplasia, one without dysplasia (Table 1) and one with dysplasia (Table 2).
#H pylori ivcd 10 code#
The median time until diagnosis of cancer among the patients with GIM was 4.6 years.Ĭurrently, there is no ICD-10-CM unique code for gastric IM. Once dysplasia is present, the location is less important as there is a higher risk regardless of location. It is believed the risk for progression into gastric cancer is highest among patients with diffuse gastric IM (which involves both antrum and body). The transformation of the cells of the gastric lining puts a person at a much higher risk of developing gastric cancer. While it is not possible to avoid some risk factors such as genetics, people can avoid other risk factors, including diet, H. pylori infection causes intestinal metaplasia, but there is also a range of risk factors that may increase the risk of developing it.

The breath test for Helicobacter pylori (H. the icd-10-cm code b96. Some healthcare professionals believe an H. CPT code 78267, 78268, 83013, 83014, 86677, 87338 Helicobacter Pylori Testing. The exact cause of intestinal metaplasia is still uncertain. Intestinal metaplasia is more common in people who have chronic acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). pylori gastritis (using CD3) ranged from 3 to 42 lymphocytes/100 epithelial cells (mean 18.5) compared to 3 to 18 lymphocytes/100 epithelial cells (mean 6.6) in the comparison group. Duodenal intraepithelial lymphocytes from patients with H. Intestinal metaplasia in the esophagus is also called Barrett’s esophagus. pylori was performed on all gastric and duodenal biopsies. pylori as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere (B96. The code B96.81 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from Octothrough Septemfor the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. View ICD-10 Tree Chapter 1 - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) Bacterial and viral infectious agents (B95-B97) Helicobacter pylori H. Research Hospitalization Volume, DRGs, Quality Outcomes, Top Hospitals & Physicians for B9681 - Helicobacter pylori H. pylori as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. Intestinal metaplasia (IM) occurs when cells in the tissues of the upper digestive tract, often in the stomach or esophagus, change and become more like cells from the intestines. B96.81 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of helicobacter pylori h.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
